The Beach Chair Position in Surgery: Beach Chair Surgical Position
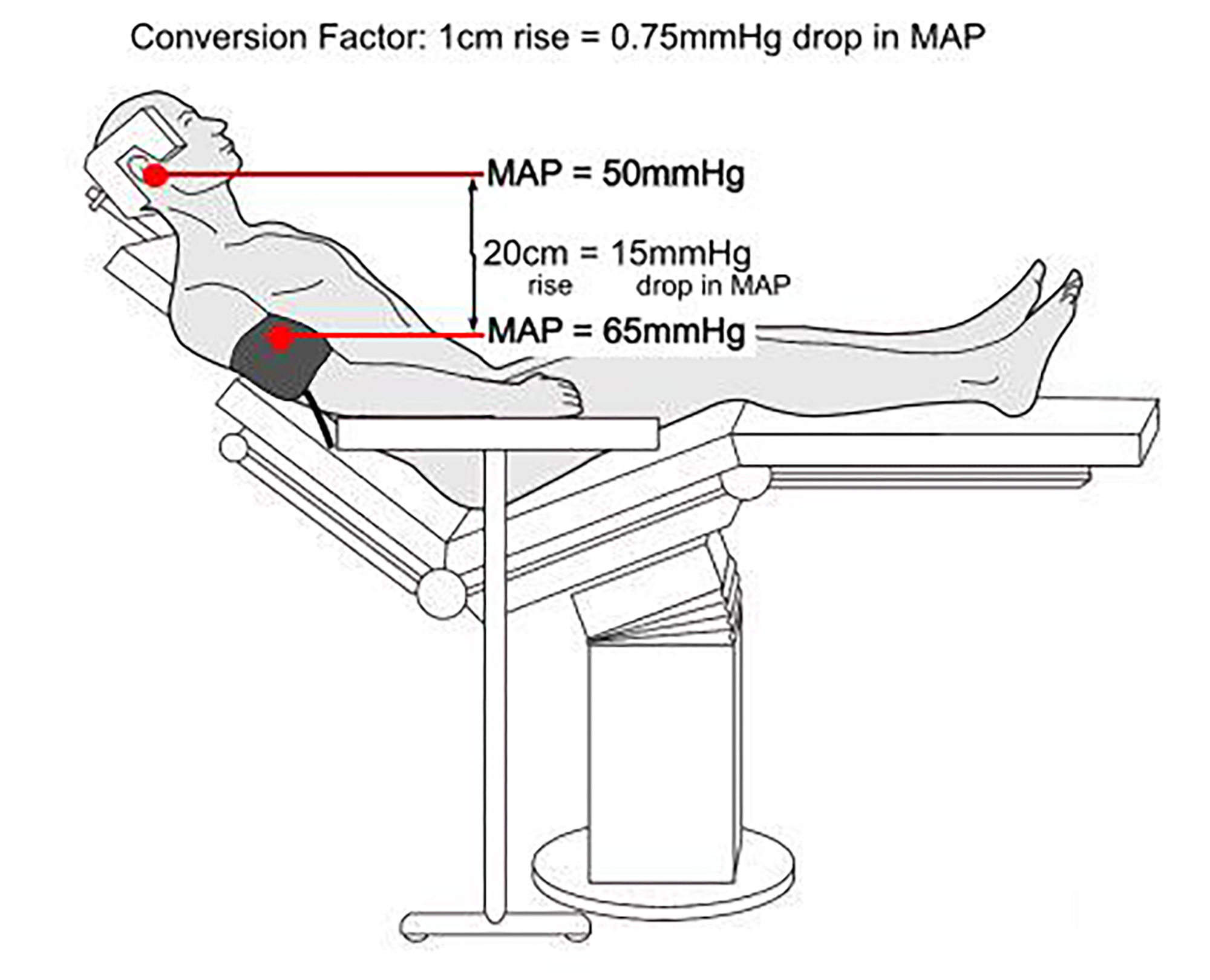
The beach chair position, also known as the semi-recumbent position, is a versatile surgical position commonly used in various surgical specialties, including spine, neurosurgery, and general surgery. It offers a unique combination of benefits for both the surgeon and the patient, but it also comes with specific considerations and potential risks that require careful management.
History and Origin
The beach chair position’s origin can be traced back to the early 20th century, when surgeons began exploring different patient positioning techniques to improve surgical access and minimize complications. The position’s name stems from its resemblance to a reclining beach chair, with the patient’s torso elevated and legs slightly bent at the knees.
Anatomical Considerations and Benefits
The beach chair position offers several anatomical benefits, making it suitable for various procedures.
- Improved Surgical Access: The elevated torso provides excellent exposure to the upper abdomen, chest, and spine, facilitating surgical procedures in these areas.
- Reduced Venous Pressure: The semi-recumbent position helps minimize venous pressure in the lower extremities, reducing the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Improved Lung Ventilation: The position promotes better lung ventilation by reducing pressure on the diaphragm, leading to improved oxygenation.
- Reduced Spinal Strain: The elevated torso helps to minimize spinal strain, which can be a concern in prolonged surgical procedures.
Potential Risks and Complications, Beach chair surgical position
While the beach chair position offers several advantages, it also comes with potential risks and complications that require careful monitoring and management.
- Airway Management Challenges: The elevated head position can make airway management more challenging, especially in patients with pre-existing airway issues.
- Venous Return Issues: The position can affect venous return, potentially leading to hypotension and reduced cardiac output, especially in patients with compromised cardiovascular function.
- Nerve Injury: Improper positioning or prolonged pressure on the extremities can lead to nerve injury, particularly in the arms and hands.
- Pressure Ulcers: Prolonged pressure on bony prominences, such as the elbows and sacrum, can increase the risk of pressure ulcers.
Proper Patient Positioning
Proper patient positioning in the beach chair position is crucial to minimize risks and optimize surgical outcomes.
- Equipment Requirements: The beach chair position requires specialized equipment, including a surgical table with adjustable sections, headrests, arm supports, and leg supports. The table should be padded to ensure patient comfort and prevent pressure ulcers.
- Safety Protocols: Before positioning the patient, it is essential to ensure that all safety protocols are followed, including proper patient identification, verification of surgical site, and obtaining informed consent.
- Patient Comfort: Patient comfort is paramount in the beach chair position. The patient should be properly padded and supported to prevent pressure points and discomfort. Regular monitoring of vital signs and assessment for any signs of discomfort are crucial.
Variations and Adaptations of the Beach Chair Position
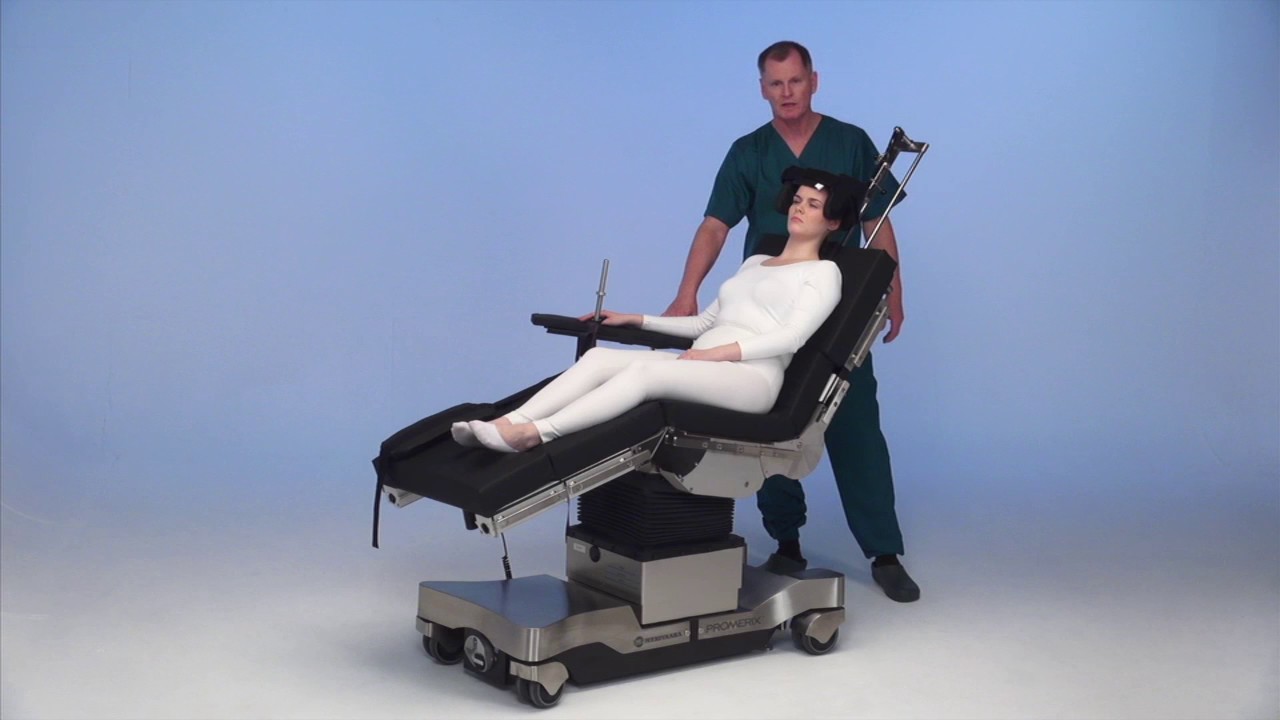
The beach chair position, while versatile, requires modifications for specific surgical procedures and patient conditions. These adaptations enhance patient safety, optimize surgical access, and improve overall comfort.
Variations in Beach Chair Positioning
Different variations of the beach chair position are employed based on the surgical procedure and the patient’s individual needs.
- Reverse Trendelenburg: This variation involves tilting the patient’s head down and elevating their feet, promoting venous return and reducing pressure on the abdomen. This is often used for procedures involving the upper abdomen or chest, such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy or thoracoscopic procedures.
- Modified Trendelenburg: In this variation, the patient’s head is slightly elevated, while the legs are lowered, facilitating drainage from the pelvic cavity and improving visualization during procedures like laparoscopic hysterectomy or colorectal surgery.
- Lateral Beach Chair: This variation positions the patient on their side, with the operative side facing upwards. This allows for better access to the lateral aspects of the body, particularly for procedures like spinal surgery or shoulder surgery.
Specialized Equipment and Accessories
Specialized equipment and accessories play a crucial role in optimizing patient positioning and safety in the beach chair position.
- Arm Boards: These provide support and immobilization for the patient’s arms, preventing injury and improving surgical access.
- Leg Straps: Securely holding the patient’s legs in place, these straps enhance stability and reduce the risk of accidental movement during surgery.
- Headrests: Adjustable headrests provide comfort and support, minimizing strain on the cervical spine.
- Pressure Relief Pads: These pads are strategically placed to reduce pressure points and prevent tissue damage, ensuring patient comfort and safety.
Clinical Scenarios for Beach Chair Position Adaptations
Adaptations to the beach chair position are often necessary in specific clinical scenarios.
- Obesity: Patients with obesity may require modifications to the beach chair position to accommodate their weight and ensure adequate surgical access. This may involve using specialized equipment like bariatric cushions and padded tables.
- Spinal Deformities: Patients with spinal deformities, such as scoliosis or kyphosis, may require custom positioning to maintain spinal alignment and prevent further injury.
- Respiratory Conditions: Patients with respiratory conditions, like asthma or COPD, may benefit from slight adjustments to the beach chair position, allowing for easier breathing and improved lung capacity.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant patients may require modifications to the beach chair position to accommodate the growing uterus and minimize pressure on the vena cava.
The beach chair surgical position, while effective for certain procedures, can sometimes feel restrictive. Imagine, instead, a gentle rocking motion, a soft embrace of comfort. That’s the feeling you get with a wooden patio glider chair , a far cry from the rigid confines of the operating room.
And while the beach chair position might be necessary for surgery, a moment of relaxation in a glider chair can be just as therapeutic, offering a soothing escape from the stress of medical procedures.
The beach chair surgical position, though seemingly simple, requires careful consideration of patient comfort and stability. Imagine the relaxed feeling of sinking into a plush chair, a feeling you can experience with the homepop modern velvet and wood chair.
This chair’s combination of velvet upholstery and sturdy wood frame offers both aesthetic appeal and practical support, much like the principles guiding the beach chair surgical position.
